Infantile cerebral palsy (ICP)
I. Definition infantile cerebral palsy
This infantile brain injury is a permanent but non-progressive medical damage to a child's premature brain. Functional impairments of the central nervous system (CNS) manifest themselves both as motor and often also as mental and behavioral disorders. It can be a combination of sensory and perceptual disorders in the brain, as well as cerebral movement disorders. Symptoms of infantile cerebral palsy vary but may lead up to paralysis in children. The causes are varied.
II. Causes of infantile cerebral palsy
Infantile cerebral palsy, also called cerebral palsy, can have many causes, which can often be identified before or during birth:
- In the womb (infectious and toxic embryo fetopathy)
- Lack of oxygen during birth
- Inflammation or trauma in the newborn age
III. Impact on patients
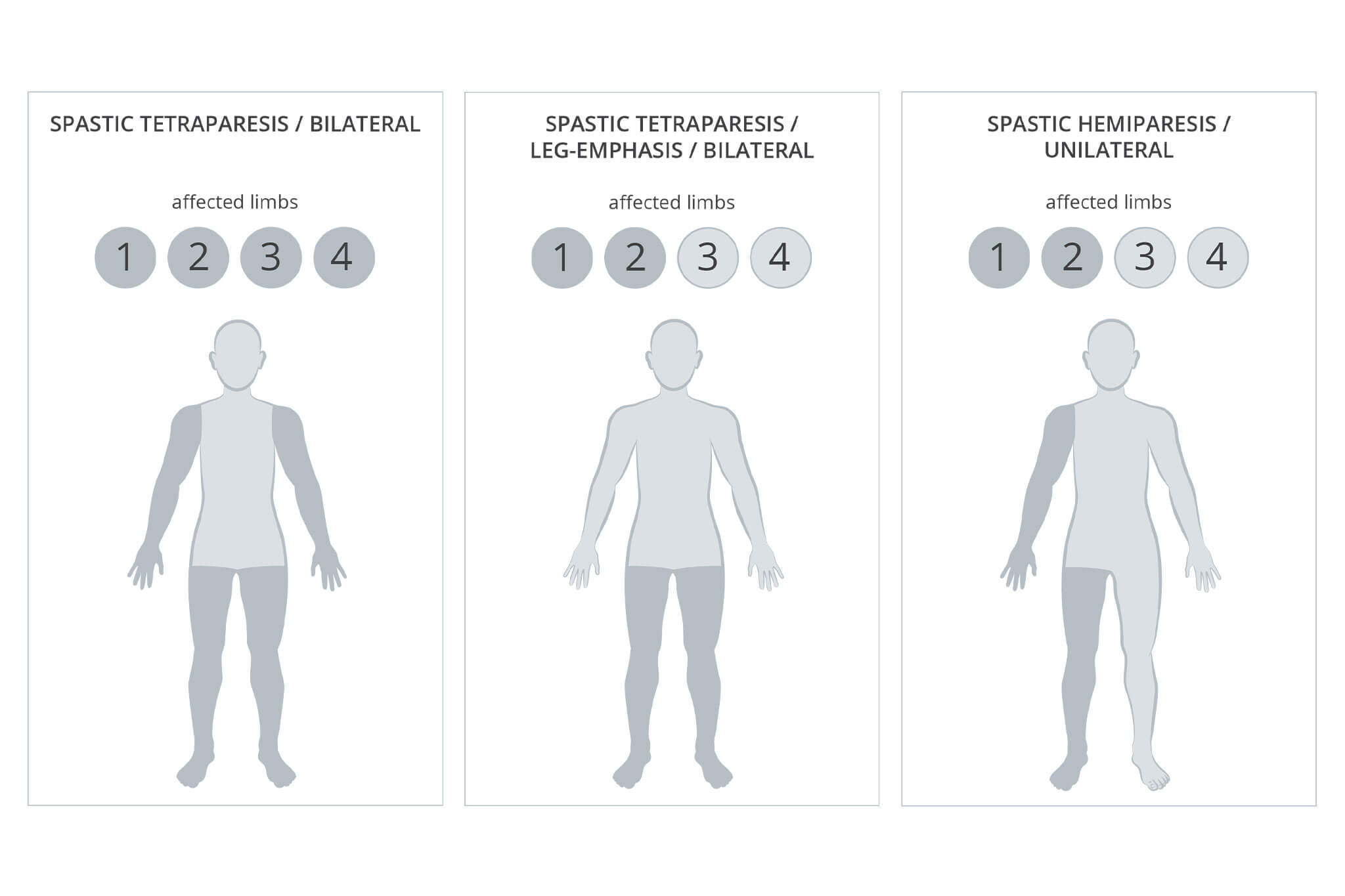
Infantile cerebral palsy takes various forms which can be summarised in following characteristics:
- Hemiplegia (unilateral spastic CP with emphasis on arms and legs)
- Both legs affected (bilateral spastic CP)
- three extremities are affected (triplegia)
- all four extremities (severe bilateral spastic CP)
Contractures
IV. Symptoms and functional impairments in infantile cerebral palsy
The medical manifestations can be summarized as movement disorders, speech disorders and sensory disorders. This can lead up to paralysis. Infantile cerebral palsy is caused by brain damage.
- Gait disturbance
- Speech disorder
- Gripping disorder
- Surface sensitivity disorder
- Deep sensory disorder
- Sensory disorder
- Cognitive disorder
V. Goal of therapy in ICP
Therapy for cerebral palsy depends on the exact characteristics and the severity of the impairment. In general, however, the following therapies can be applied:- Promoting development and maturation
- Growth guidance
- Pain prevention
- Function improvement
- Improvement of motor skills
VI. Course of the ICP
There are three different forms, which may eb mixed:- Spasticity 80-90%
- Involuntary movements (dyskinesia) 6%
- Trembling movements (ataxia) 5%