NEURO – orthoses for neurological indications
Neurological diseases often affect the entire body and can therefore also affect the musculoskeletal system. For example, neurological indications can affect muscle tone. If the muscle tension is too high, spasticity occurs, which can also lead to a contracture of the joint. In this case, functionality will be restricted.
Independent participation in active life as well as nursing are made more difficult in this case. Pain can also occur. In return, a neurological indication can also lead to reduced muscle tension. If the neuronal control of the muscle is affected, muscles can no longer be consciously moved.
Neurological indications are diverse and complex. For this reason, the support that orthopaedic devices offer is varied. Orthoses and bandages may exert an external influence on the musculoskeletal system in both neurology and orthopaedics. In therapy to stretch shortened muscles as well as in everyday life to support function .
Even if the definition of an impairment is that it cannot be cured, devices can contribute to pain reduction and functional improvement. Depending on the objective, mobilization and participation in active life, improved care or pain relief can be achieved.
Independent participation in active life as well as nursing are made more difficult in this case. Pain can also occur. In return, a neurological indication can also lead to reduced muscle tension. If the neuronal control of the muscle is affected, muscles can no longer be consciously moved.
Neurological indications are diverse and complex. For this reason, the support that orthopaedic devices offer is varied. Orthoses and bandages may exert an external influence on the musculoskeletal system in both neurology and orthopaedics. In therapy to stretch shortened muscles as well as in everyday life to support function .
Even if the definition of an impairment is that it cannot be cured, devices can contribute to pain reduction and functional improvement. Depending on the objective, mobilization and participation in active life, improved care or pain relief can be achieved.
Orthoses to support neurological rehabilitation
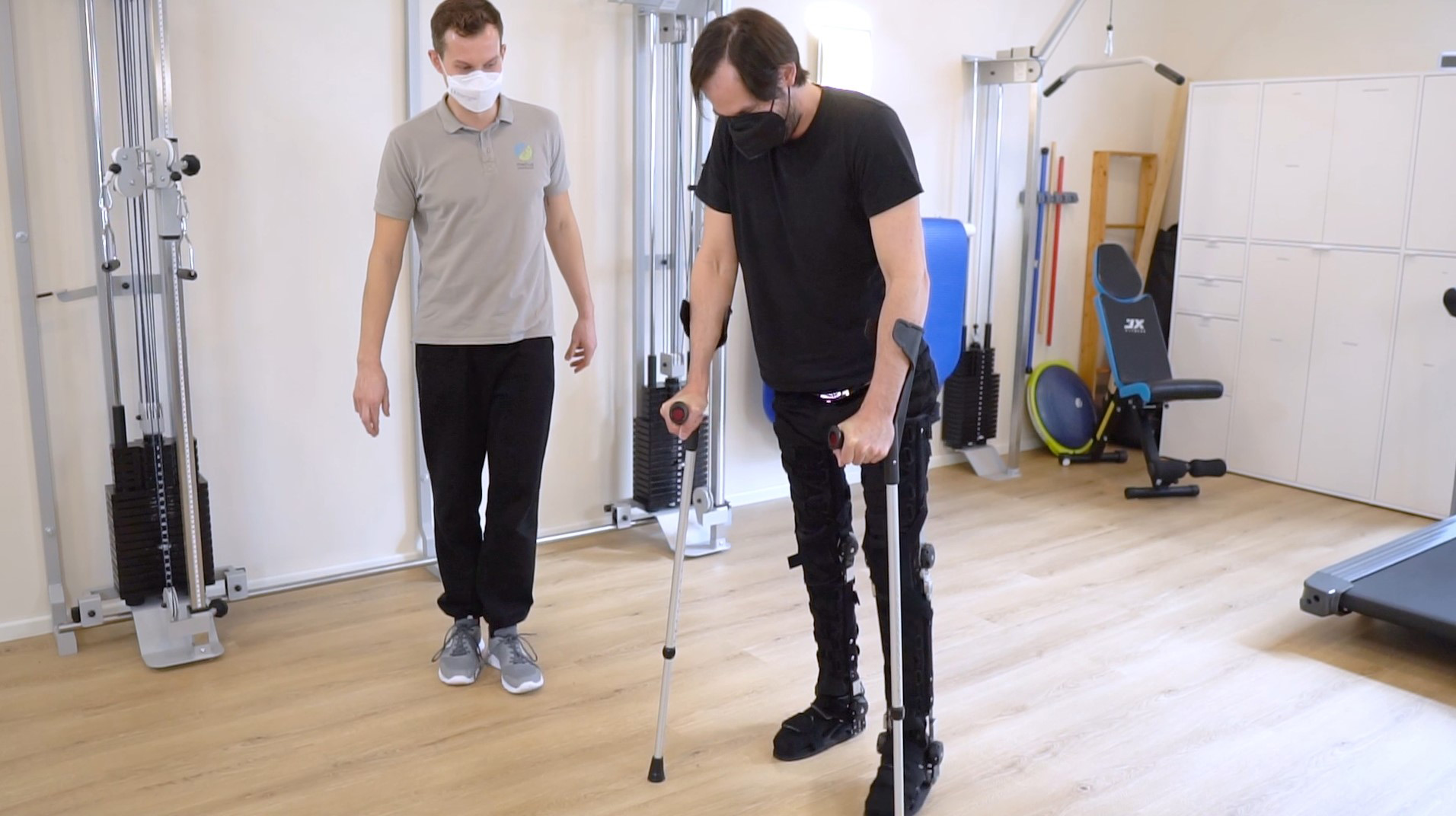
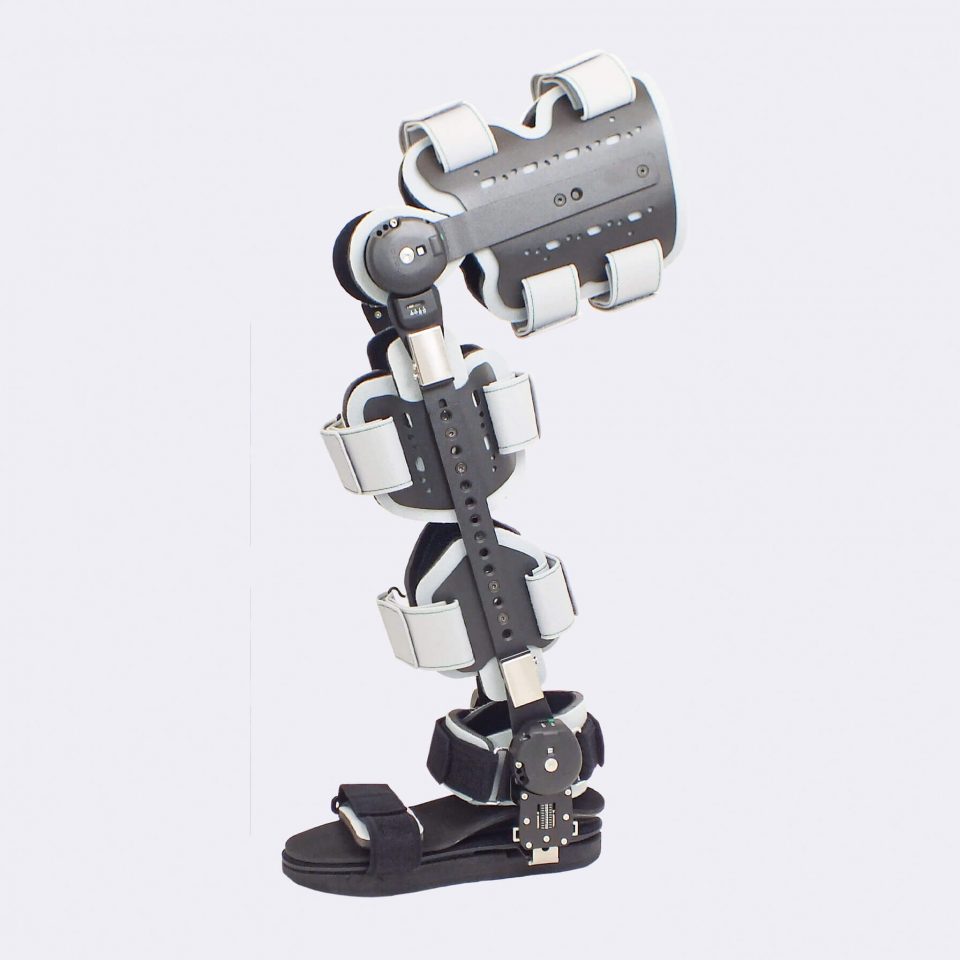
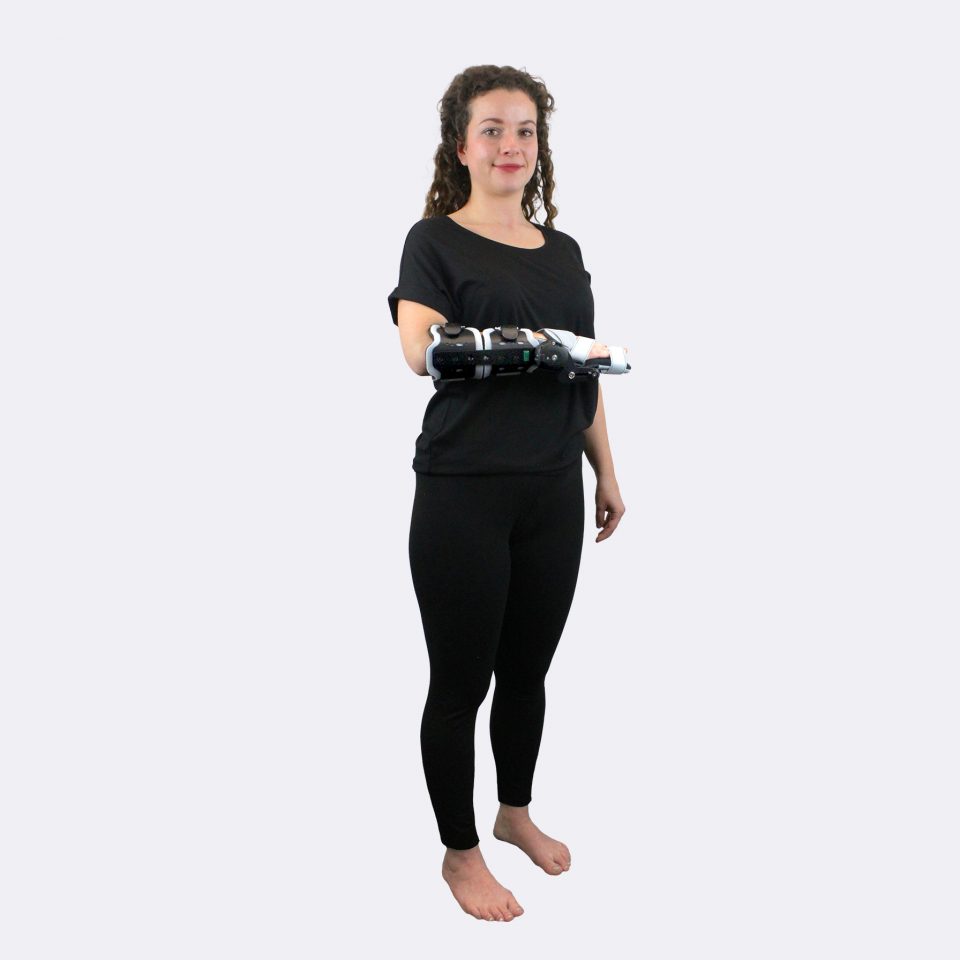
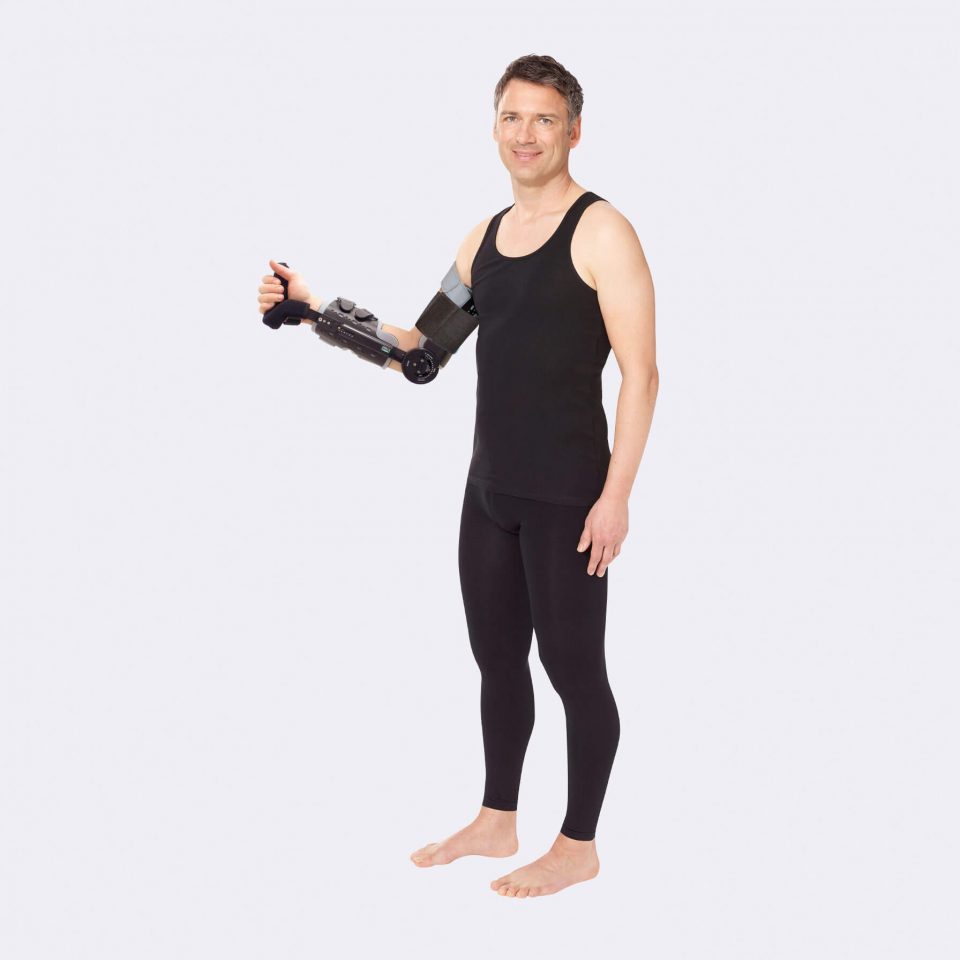
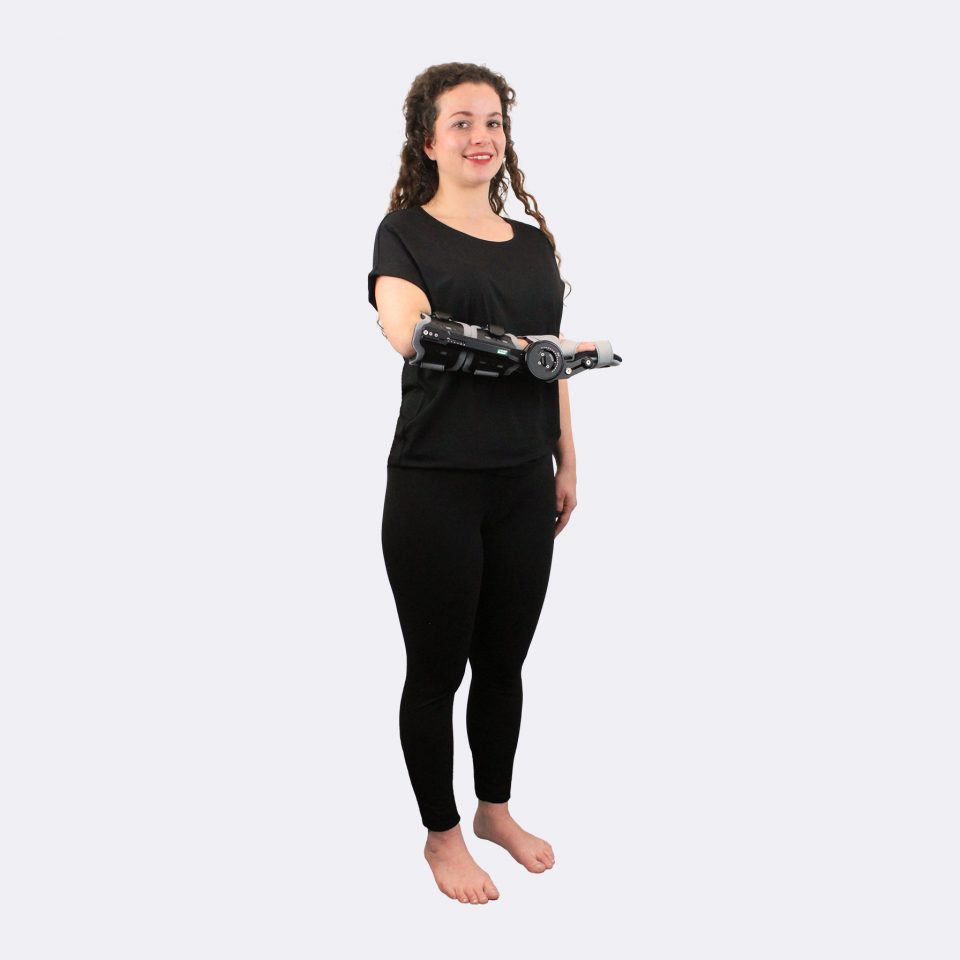
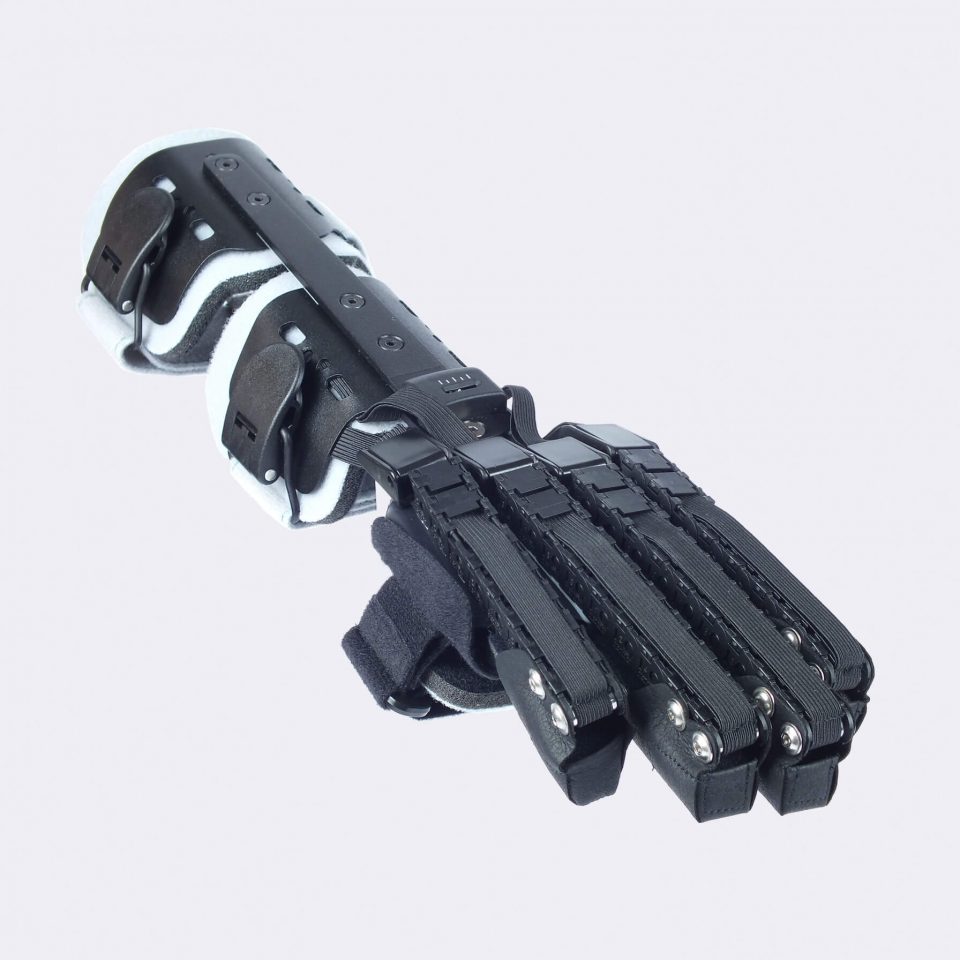
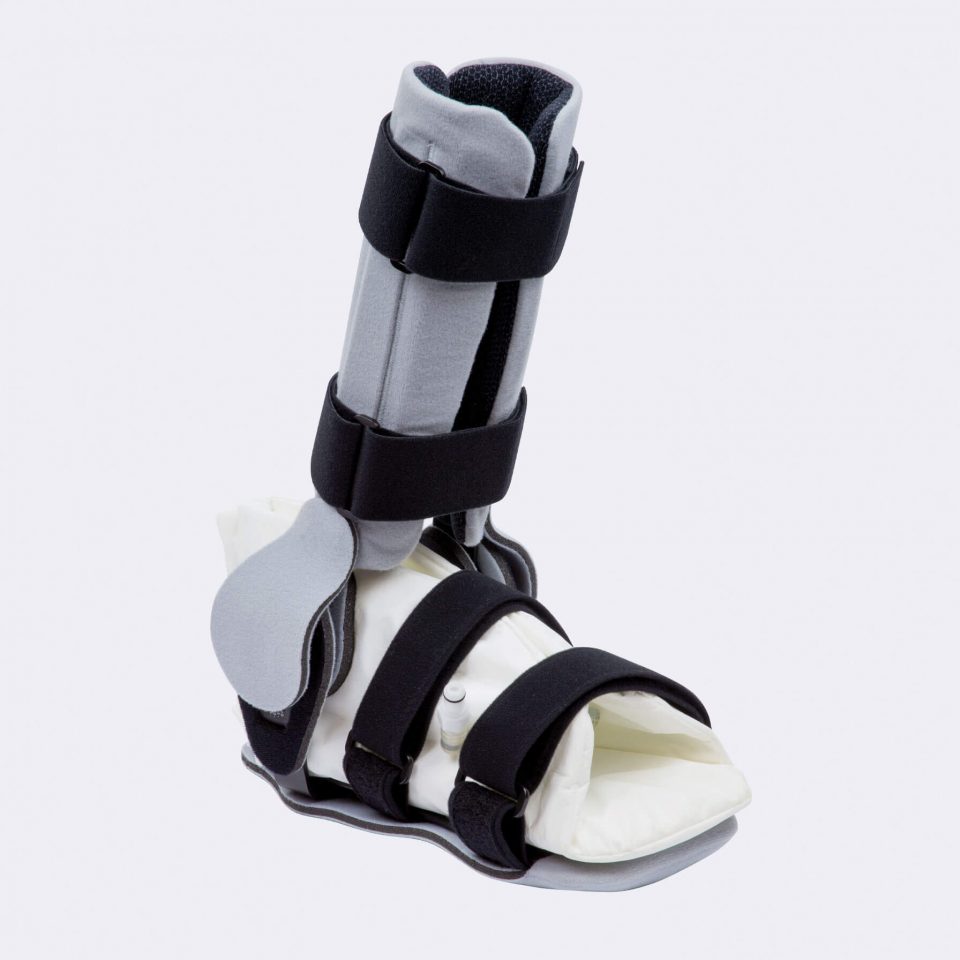
Our CDS® orthoses are based on the principle of dynamic redression. The spring-based CDS® hinges stretch muscles in a controlled and therefore careful manner. Unlike static whining, our CDS® orthoses work dynamically via controllable spring force, which can be adapted to the course of treatment of the patient.
The spring mechanism stretches the shortened structures while allowing movement. This promotes blood circulation in the tissue and prevents new contractures. In addition, the muscle can experience spasms, which is a decisive advantage, especially in neurological indications. After the spasm, the muscle is gently guided back into relaxation.
The spring mechanism stretches the shortened structures while allowing movement. This promotes blood circulation in the tissue and prevents new contractures. In addition, the muscle can experience spasms, which is a decisive advantage, especially in neurological indications. After the spasm, the muscle is gently guided back into relaxation.
The spring force is adjustable and can be adapted to the patient and the course of treatment. The same applies to the redression range. This avoids painful and harmful overstretching and increases patient compliance.
The CDS® joints can support the therapists in their work. Regular wearing of a CDS® orthosis can, for example, stabilize the therapy result until the next unit or prepare for therapy.
The CDS® joints can support the therapists in their work. Regular wearing of a CDS® orthosis can, for example, stabilize the therapy result until the next unit or prepare for therapy.
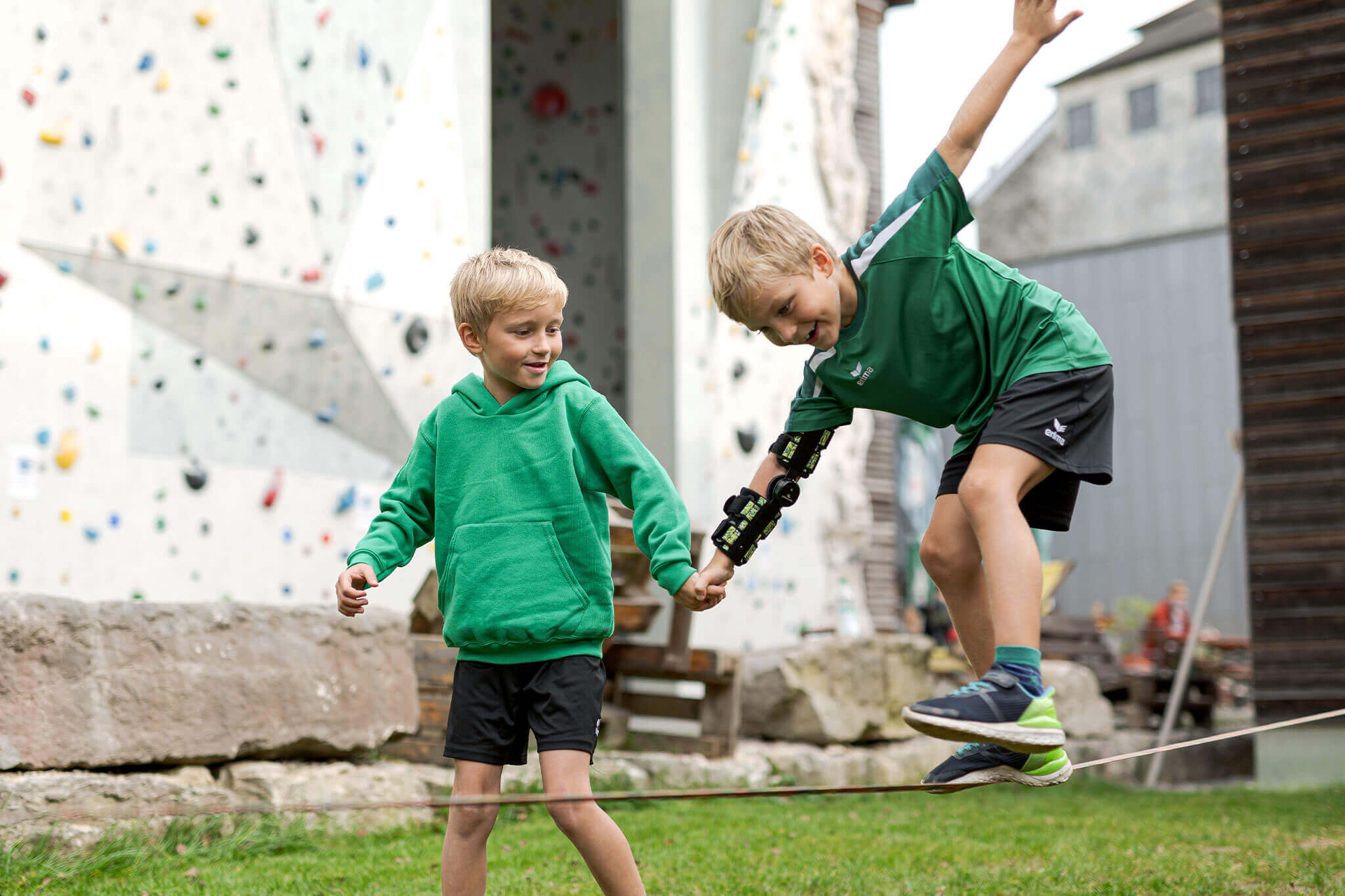

Orthoses for functional support
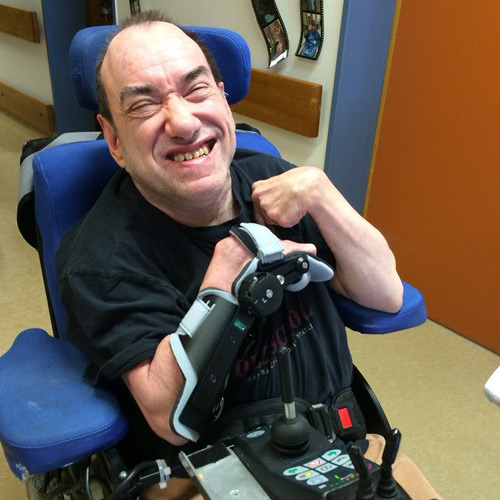
As part of a functional rehabilitation, our orthoses can also be used to support and stabilize functionality. The stabilizing effect of our devices enables patients to carry out guided movements safely. Here the technicians need to clarify to what extent safe use can be guaranteed.Our orthoses to support neurological rehabilitation
- The brace applies a dynamic low load prolonged stretch to stimulate growth in the contracted tissue.